Spring Bean的生命周期由多个特定的生命队段组成,可以从两个层面来定义Bean的生命周期。第一层是Bean的作用范围;第二层是实例化Bean所经历的一系列阶段。
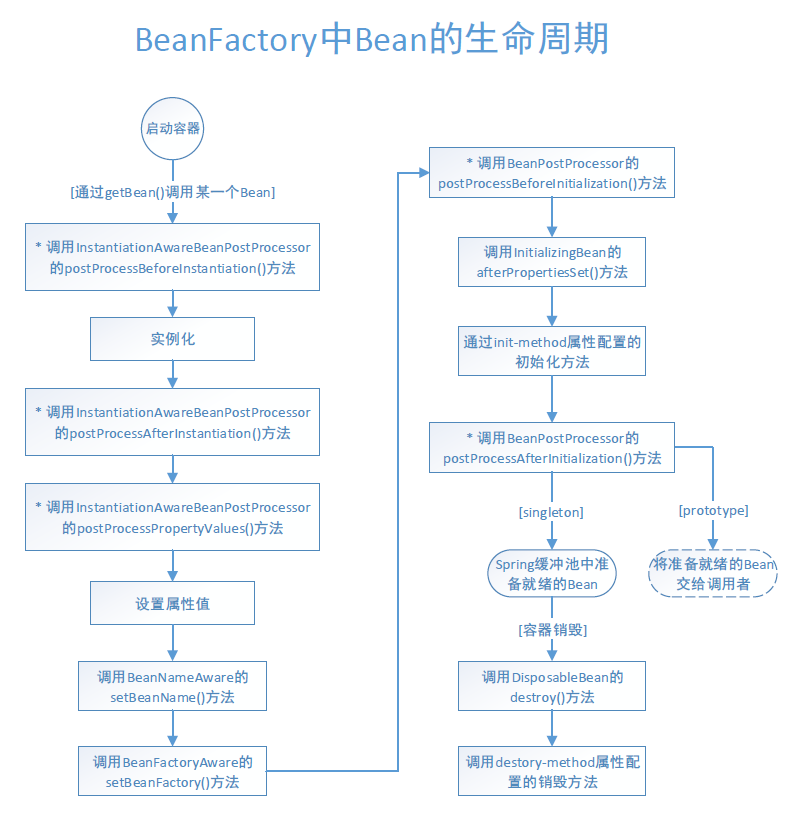
BeanFactory中Bean 的生命周期
BeanFactory对Bean的初始化并不是在启动IoC容器时,是在被第一次调用的时候。BeanFactory对于单例(默认singleton)的Bean会进行缓存,第二次用时直接取。
Spring在DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry类中提供了一个用于缓存单例Bean的缓存器,是一个用HashMap实现的缓存器,单例的Bean以beanName为键保存这在这个HashMap中。
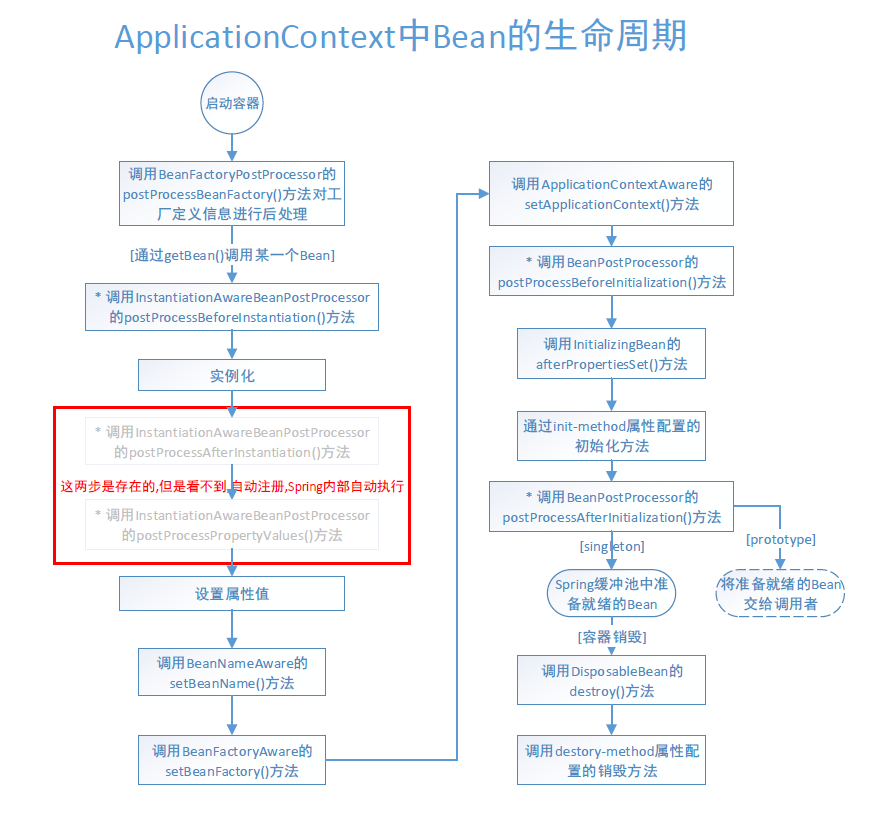
ApplicationContext中Bean 的生命周期
ApplicationContext则在初始化应用上下文时就实例化所有单例的Bean。如果设置了lazy-init=”true”后,则执行的是懒加载策略,IoC容器启动就不会马上实例化,而是在被调用时实例化。
Bean在应用上下文中的生命周期与在BeanFactory中的生命周期相似,不同的是,如果Bean实现了org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware接口,则会增加一个调用该接口方法setApplicationContext()的步骤。- 如果在配置文件(
bean.xml)声明了工厂后处理器接口BeanFactoryPostProcessor的实现类,则应用在上下文装载配置文件之后,初始化Bean实例之前将调用postProcessBeanFactory()方法对配置信息进行后处理。工厂后处理器是容器级的,只在应用上下文初始化时调用一次,其目的是完成一些配置文件的加工处理工作。
- 另一个不同是ApplicationContext会利用反射机制自动识别出配置文件中定义的
BeanPostProcessor,InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,BeanFactoryPostProcessor,并自动将它们注册到应用上下文中;而BeanFactory需要在代码中手工调用addBeanPostProcessor()方法进行注册。
这些是在应用开发中普遍使用ApplicationContext,而很少使用BeanFactory的原因之一。
- 在ApplicationContext中,只需要配置文件中定义工厂后处理器和Bean后处理器,它们就会按预期的方式运行。
示例代码
BeanFactory
- Bean
实现BeanFactoryAware, BeanNameAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
| package com.smart.beanfactory;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
public class Car implements BeanFactoryAware, BeanNameAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
private String brand;
private String color;
private int maxSpeed;
private String name;
private BeanFactory beanFactory;
private String beanName;
public Car() {
System.out.println("调用Car()构造函数。");
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
System.out.println("调用setBrand()设置属性。");
this.brand = brand;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public int getMaxSpeed() {
return maxSpeed;
}
public void setMaxSpeed(int maxSpeed) {
this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed;
}
public void introduce(){
System.out.println("introduce:"+this.toString());
}
public String toString() {
return "brand:" + brand + "/color:" + color + "/maxSpeed:"+ maxSpeed;
}
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("调用BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory()。");
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
public void setBeanName(String beanName) {
System.out.println("调用BeanNameAware.setBeanName()。");
this.beanName = beanName;
}
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("调用InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()。");
}
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("调用DisposableBean.destory()。");
}
public void myInit() {
System.out.println("调用myInit(),将maxSpeed设置为240。");
this.maxSpeed = 240;
}
public void myDestory() {
System.out.println("调用myDestroy()。");
}
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("调用setApplicationContext方法");
}
}
|
- MyBeanPostProcessor
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| package com.smart.beanfactory;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import com.smart.beanfactory.Car;
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor{
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if(beanName.equals("car")){
Car car = (Car)bean;
if(car.getMaxSpeed() >= 200){
System.out.println("调用MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(),将maxSpeed调整为200。");
car.setMaxSpeed(200);
}
}
return bean;
}
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if(beanName.equals("car")){
Car car = (Car)bean;
if(car.getColor() == null){
System.out.println("调用MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(),color为空,设置为默认黑色。");
car.setColor("黑色");
}
}
return bean;
}
}
|
- MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| package com.smart.beanfactory;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValues;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter;
public class MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor extends InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter{
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if("car".equals(beanName)){
System.out.println("MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInstantiation");
}
return null;
}
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if("car".equals(beanName)){
System.out.println("InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInstantiation");
}
return true;
}
public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(
PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
if("car".equals(beanName)){
System.out.println("InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessPropertyValues");
}
return pvs;
}
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
}
|
- MainBeanFactory
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| package com.smart.beanfactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
public class MainBeanFactory {
private static void LifeCycleInBeanFactory(){
Resource res = new ClassPathResource("com/smart/beanfactory/beans.xml");
BeanFactory bf= new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader((DefaultListableBeanFactory)bf);
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(res);
((ConfigurableBeanFactory)bf).addBeanPostProcessor(new MyBeanPostProcessor());
((ConfigurableBeanFactory)bf).addBeanPostProcessor(
new MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor());
Car car1 = (Car)bf.getBean("car");
car1.introduce();
car1.setColor("红色");
Car car2 = (Car)bf.getBean("car");
System.out.println("car1==car2:"+(car1==car2));
((DefaultListableBeanFactory)bf).destroySingletons();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LifeCycleInBeanFactory();
}
}
|
- bean.xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd">
<bean id="car" class="com.smart.beanfactory.Car"
init-method="myInit"
destroy-method="myDestory"
p:brand="红旗CA72"
p:maxSpeed="200"/>
</beans>
|
- 执行结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInstantiation
调用Car()构造函数。
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInstantiation
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessPropertyValues
调用setBrand()设置属性。
调用BeanNameAware.setBeanName()。
调用BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory()。
调用MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(),color为空,设置为默认黑色。
调用InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()。
调用myInit(),将maxSpeed设置为240。
调用MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(),将maxSpeed调整为200。
introduce:brand:红旗CA72/color:黑色/maxSpeed:200
car1==car2:true
调用DisposableBean.destory()。
调用myDestroy()。
|
ApplicationContext
- Bean
实现BeanFactoryAware, BeanNameAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean, ApplicationContextAware接口。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
| package com.smart.context;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
public class Car implements BeanFactoryAware, BeanNameAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean, ApplicationContextAware {
private String brand;
private String color;
private int maxSpeed;
private String name;
private BeanFactory beanFactory;
private String beanName;
public Car() {
System.out.println("调用Car()构造函数。");
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
System.out.println("调用setBrand()设置属性。");
this.brand = brand;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public int getMaxSpeed() {
return maxSpeed;
}
public void setMaxSpeed(int maxSpeed) {
this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed;
}
public void introduce(){
System.out.println("introduce:"+this.toString());
}
public String toString() {
return "brand:" + brand + "/color:" + color + "/maxSpeed:"+ maxSpeed;
}
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("调用BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory()。");
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
public void setBeanName(String beanName) {
System.out.println("调用BeanNameAware.setBeanName()。");
this.beanName = beanName;
}
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("调用InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()。");
}
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("调用DisposableBean.destory()。");
}
public void myInit() {
System.out.println("调用myInit(),将maxSpeed设置为240。");
this.maxSpeed = 240;
}
public void myDestory() {
System.out.println("调用myDestroy()。");
}
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("调用setApplicationContext方法");
}
}
|
- MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| package com.smart.context;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor{
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory bf) throws BeansException {
BeanDefinition bd = bf.getBeanDefinition("car");
bd.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("brand", "奇瑞QQ");
System.out.println("调用MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory()!");
}
}
|
- MyBeanPostProcessor
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| package com.smart.context;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor{
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if(beanName.equals("car")){
Car car = (Car)bean;
if(car.getColor() == null){
System.out.println("调用MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(),color为空,设置为默认黑色。");
car.setColor("黑色");
}
}
return bean;
}
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if(beanName.equals("car")){
Car car = (Car)bean;
if(car.getMaxSpeed() >= 200){
System.out.println("调用MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(),将maxSpeed调整为200。");
car.setMaxSpeed(200);
}
}
return bean;
}
}
|
- MainApplicationContext
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| package com.smart.context;
import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MainApplicationContext {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AbstractApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/smart/context/bean.xml");
Car car =ctx.getBean("car",Car.class);
Car car1 =ctx.getBean("car",Car.class);
System.out.println("car == car1 : " + (car == car1));
ctx.close();
}
}
|
- bean.xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd">
<bean id="car" class="com.smart.context.Car" init-method="myInit" destroy-method="myDestory"
p:brand="红旗CA72"
p:maxSpeed="200"/>
<bean id="myBeanPostProcessor" class="com.smart.context.MyBeanPostProcessor"></bean>
<bean id="myBeanFactoryPostProcessor" class="com.smart.context.MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor"></bean>
</beans>
|
- 执行结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| 调用MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory()!
调用Car()构造函数。
调用setBrand()设置属性。
调用BeanNameAware.setBeanName()。
调用BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory()。
调用setApplicationContext方法
调用MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(),color为空,设置为默认黑色。
调用InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()。
调用myInit(),将maxSpeed设置为240。
调用MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(),将maxSpeed调整为200。
car == car1 : true
三月 19, 2018 12:13:40 上午 org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext doClose
信息: Closing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@71be98f5: startup date [Mon Mar 19 00:13:39 CST 2018]; root of context hierarchy
调用DisposableBean.destory()。
调用myDestroy()。
|
代码GitHub
验证代码GitHub库:SpringBeanLifecycle
SpringBeanLifecycle



