创建 Spring Boot 应用,默认会添加 Maven 插件:spring-boot-maven-plugin。如果该应用的结构比较简单,使用默认的编译打包等,可以不用额外的配置。
若应用结构比较复杂,如父子工程,多层结构等;或要通过命令行动态指定打包方式等等,就需要额外的配置支持了。
该篇结合官方文档对 spring-boot-maven-plugin 的使用配置进行详细描述。另有的 Maven 相关文章 ,但不是针对 Spring Boot 和 插件的。
Spring Boot Maven Plugin 官网 ,Apache Maven 官网 。
Spring Boot Maven Plugin 为 Spring Boot 在 Maven 中提供支持,允许将应用打成可执行的 jar 包或 war包,并可 就地 运行应用。
介绍 Goals 此插件有以下可用的目标(Goal:可理解插件的意图):
Goal
描述
备注
spring-boot:build-info 根据当前 MavenProject 的内容生成一个build-info.properties文件。
生成构建信息以便被监控使用。
spring-boot:help 在 spring-boot-maven-plugin 上显示帮助信息。mvn spring-boot:help -Ddetail=true -Dgoal=<goal-name>来显示参数详情。
spring-boot:repackage 重新打包现有的 JAR 和 WAR 包,以便可以使用 java -jar 命令行来运行。 layout = NONE也可以简单地用于打包具有嵌套依赖关系的 JAR(并且没有主类,因此不是可执行文件)。
spring-boot:run 运行一个可执行的应用。
spring-boot:start 启动 Spring 应用程序。 与run目标相反,这不会阻止并允许其他目标在应用程序上运行。
与 stop一起管理 Spring Boot 应用的生命周期(例如,集成 test)
spring-boot:stop 停止已由 start 目标启动的 Spring 应用程序。 通常在测试套件完成后调用。
在基于 IDEA 开发 Maven 工程的 Spring Boot 应用时,Maven 自身提供了生命周期管理,且更强大和智能,自动拉取依赖等。使用 spring-boot-maven-plugins,在 IDEA 的 Maven 工具栏也可以看到提供了一个 Plugins的生命周期管理。
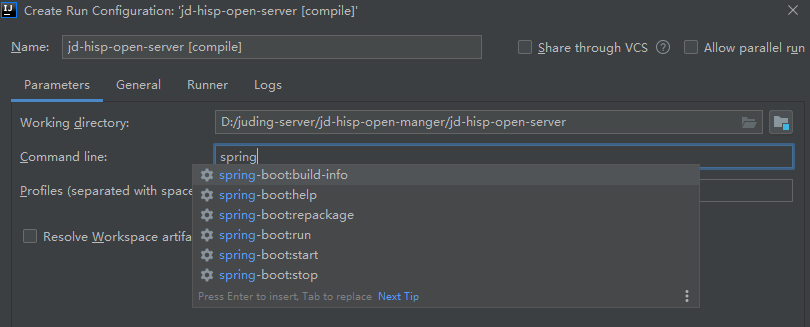
基于 IDEA ,也可以自己创建 Maven 运行配置,命令行就是上面的目标,如下图;也可以使用 Maven 命令在命令行窗口执行目标命令,如:mvn spring-boot:run。
系统要求 以下指定了运行此 Maven 插件的最低要求:
Dependency
Requirements
Maven
2.0
JDK
1.8
Memory
No minimum requirement.
Disk Space
No minimum requirement.
引入插件 如果创建的是 Spring Boot 应用,默认会在 pom.xml 文件中引入此插件,省略以下操作。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 <project > ... <build > <pluginManagement > <plugins > <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <version > 2.2.6.RELEASE</version > </plugin > ... </plugins > </pluginManagement > <plugins > <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <version > 2.2.6.RELEASE</version > </plugin > ... </plugins > </build > ... </project >
可以在项目的插件配置中指定版本,而 Spring Booot 的版本默认了相关组件,插件的版本,可以不额外指定版本号。
插件用法 该插件提供了几个目标来与 Spring Boot 应用程序一起工作:
Repackaging 若要重新打包的应用,只需要在 pom.xml 中添加对该插件的引用:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 <build > ... <plugins > ... <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <version > 2.2.7.RELEASE</version > <executions > <execution > <goals > <goal > repackage</goal > </goals > </execution > </executions > </plugin > ... </plugins > ... </build >
上面的示例重新打包了在 Maven 生命周期的打包阶段构建的 jar 或 war,包括项目中定义的所有提供的依赖项。 如果其中一些依赖项需要排除,则可以使用排除选项之一,有关更多详细信息,请参见排除依赖项 。 请注意,maven-war-plugin插件目录还不支持 outputFileNameMapping功能。
默认情况下,会自动排除 Devtools (可以使用 excludeDevtools 属性进行控制)。 为了使它与 war 打包一起使用,必须将 spring-boot-devtools 依赖项设置为 optional 或将 scope设置为provided 。
默认情况下,原始(即不可执行)artifact 被重命名为以**.original**为后缀的文件,但也可以使用自定义分类器保留原始 **artifact **。
该插件会重写您的清单,特别是它管理 **Main-Class **和 Start-Class 元素。因此,如果默认设置不起作用,则必须在其中进行配置(不在jar插件中)。 清单中的 Main-Class 实际上是由启动插件的 layout 属性控制的,例如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 <build > ... <plugins > ... <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <version > 2.2.7.RELEASE</version > <configuration > <mainClass > ${start-class}</mainClass > <layout > ZIP</layout > </configuration > <executions > <execution > <goals > <goal > repackage</goal > </goals > </execution > </executions > </plugin > ... </plugins > ... </build >
layout 属性默认为基于存档类型(jar 或 war )的评估。 提供以下布局:
JAR:常规的可扫许 JAR。WAR:可扫许 WAR。provided 依赖项放在 WEB-INF/lib-provided 中,以避免 war 包部署到 Servlet 容器中发生冲突。ZIP(DIR的别名):类似于 JAR使用了 PropertiesLauncher。NONE:捆绑所有依赖项和项目资源。不捆绑引导加载程序(bootstrap loader)。
Running 该插件包含一个运行目标(run goal),可用于从命令行启动的应用程序:
默认情况下,应用程序是在分支过程中执行的,并且在命令行上设置属性不会影响该应用程序。
如果需要指定一些JVM 参数(即用于调试目的),则可以使用 jvmArguments 参数。有关更多详细信息,请参见调试应用程序 ,还明确支持系统属性(system properties )和环境变量(environment variables )。
通常会启用配置文件(profile),因此有用于指定专用的配置文件 的属性,它提供了-Dspring-boot.run.jvmArguments ="-Dspring.profiles.active = dev"的快捷方式,请参阅指定活动配置文件 。
尽管不建议这样做,但是可以通过禁用 fork 属性直接从 Maven JVM 执行应用程序。 这样做意味着将忽略jvmArguments,systemPropertyVariables,environmentVariables和agent选项。
Spring Boot 1.3 开始引入了 devtools,该模块可改善在 Spring Boot 应用程序上工作时的开发时间体验。 要启用它,只需将以下依赖项添加到您的项目中:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-devtools</artifactId > <version > 2.2.7.RELEASE</version > <optional > true</optional > </dependency > </dependencies >
当 devtools正在运行时,它会在重新编译应用程序时检测到更改并自动刷新它。 这不仅适用于资源,而且适用于代码。 它还提供了一个 LiveReload 服务器,以便它可以在发生任何变化时自动触发浏览器刷新。
还可以将 Devtools 配置为仅在静态资源发生更改时刷新浏览器(并忽略代码中的任何更改)。 只需在项目中包括以下属性:
1 spring.devtools.remote.restart.enabled =false
在 devtools 之前,该插件默认情况下支持资源的热刷新 ,现在已禁用它,以支持上述解决方案。 您可以通过配置项目随时还原它:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 <build > ... <plugins > ... <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <version > 2.2.7.RELEASE</version > <configuration > <addResources > true</addResources > </configuration > </plugin > ... </plugins > ... </build >
当启用了 addResources,当运行应用程序时,任何src/main/resources文件夹都将添加到应用程序类路径(classpath)中,并且在(target/classes)中发现的所有重复项都将被删除。
这样可以热刷新资源,这在开发Web应用程序时非常有用。 例如,可以处理 HTML,CSS 或 JavaScript 文件,并且无需重新编译应用程序即可立即查看更改后的效果。 这也是允许前端开发人员工作在无需下载和安装 Java IDE 的一种有用方法。
请注意,使用此功能的副作用是在构建时无法进行资源过滤。
为了与重新打包(repackage)目标保持一致,运行(run)目标以这样的方式构建类路径:将插件配置中排除的任何依赖项也从类路径中排除。 有关更多详细信息,请参见排除依赖项 。
有时在运行应用程序时包含测试依赖项很有用。 例如,如果要在使用测试桩类 的测试模式下运行应用程序。 如果希望这样做,可以将useTestClasspath参数设置为true。 请注意,这仅在运行应用程序时适用:重新打包目标不会将测试依赖项添加到生成的JAR / WAR 中。
集成 Test 虽然可以从测试(或测试套件)本身非常轻松地启动 Spring Boot 应用程序,但可能需要在构建本身中进行处理。
为了确保围绕集成测试正确管理 Spring Boot 应用程序的生命周期,可以使用如下所述的开始(start)和停止(stop)目标:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 <build > ... <plugins > ... <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <version > 2.2.7.RELEASE</version > <executions > <execution > <id > pre-integration-test</id > <goals > <goal > start</goal > </goals > </execution > <execution > <id > post-integration-test</id > <goals > <goal > stop</goal > </goals > </execution > </executions > </plugin > ... </plugins > ... </build >
现在,这种设置可以使用 failsafe-plugin 按预期运行集成测试。
还可以配置更高级的设置,以在设置了特定属性时跳过集成测试:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 <properties > <it.skip > false</it.skip > </properties > <build > <plugins > <plugin > <groupId > org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId > <artifactId > maven-failsafe-plugin</artifactId > <configuration > <skip > ${it.skip}</skip > </configuration > </plugin > <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <version > 2.2.7.RELEASE</version > <executions > <execution > <id > pre-integration-test</id > <goals > <goal > start</goal > </goals > <configuration > <skip > ${it.skip}</skip > </configuration > </execution > <execution > <id > post-integration-test</id > <goals > <goal > stop</goal > </goals > <configuration > <skip > ${it.skip}</skip > </configuration > </execution > </executions > </plugin > </plugins > </build >
如果运行mvn verify -Dit.skip = true,则将完全跳过集成测试。
打包流程 mvn package spring-boot-maven-plugin插件可以理解为是对 mvn package命令进行了二次封装,在其基于上增加了适配于 Spring Boot 项目的 Maven 命令(目标:Goals),目的是对 Maven 打出的原始包进行二次修改,例如重新打包成可执行文件等。
命令执行后会在创建的 target 目录中会生成 2 个文件:
*.jar:可执行 jar,包含 pom 中的所有依赖,可直接用 java -jar命令执行。*.jar.original:是 Maven 在 Spring Boot 重新打包(repackage)之前创建的原始 jar文件,只有少量的用户类,不包含依赖。
如果是 Spring boot 项目( 使用了 spring-boot-starter-parent包),默认在执行 mvn package包时会执行 spring boot repackage 操作(即 默认 ID 为 repackage 的目标为 repackage ,且自动执行)。
执行 mvn package 打包命令后,先是执行的 mvn 常规操作,创建普通 jar包,然后 spring boot repackage 将其重新命名为 *.jar.original原始包, 在原始包的基础上添加项目依赖和起动类,最后打成可执行的 jar包。如下日志:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 mvn package -Dmaven.test.skip=true [INFO] Scanning for projects... [INFO] [INFO] -----------------< com.gxitsky.file.server:file-server >----------------- [INFO] Building file-server 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT [INFO] --------------------------------[ jar ]--------------------------------- [INFO] [INFO] --- maven-resources-plugin:3.1.0:resources (default-resources) @ file-server --- [INFO] Using 'UTF-8' encoding to copy filtered resources. [INFO] Copying 1 resource [INFO] Copying 0 resource [INFO] [INFO] --- maven-compiler-plugin:3.8.1:compile (default-compile) @ file-server --- [INFO] Nothing to compile - all classes are up to date [INFO] [INFO] --- maven-resources-plugin:3.1.0:testResources (default-testResources) @ file-server --- [INFO] Not copying test resources [INFO] [INFO] --- maven-compiler-plugin:3.8.1:testCompile (default-testCompile) @ file-server --- [INFO] Not compiling test sources [INFO] [INFO] --- maven-surefire-plugin:2.22.2:test (default-test) @ file-server --- [INFO] Tests are skipped. [INFO] [INFO] --- maven-jar-plugin:3.1.2:jar (default-jar) @ file-server --- [INFO] Building jar: D:\gxitsky-server\file-server\target\file-server-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar [INFO] [INFO] --- spring-boot-maven-plugin:2.2.5.RELEASE:repackage (repackage) @ file-server --- [INFO] Replacing main artifact with repackaged archive [INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------ [INFO] BUILD SUCCESS [INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------ [INFO] Total time: 2.544 s [INFO] Finished at: 2020-05-11T17:07:04+08:00 [INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
打成普通Jar 如果是 Spring Boot 项目结构是通过父子工程来管理,就可能有多个层级结构,工程之前存在依赖关系,如果所依赖的包被打包 spring boot 的可执行 jar,则该工程中启动时就会报找不到类的异常。具体原因见下面的 使用原始包 小节内容。
此时需要将所依赖的包打包普通 jar 包,即不要执行 spring-boot.repackage操作。如下操作:
1 mvn clean package -D spring-boot.repackage.skip=true
或在 pom.xml文件中配置将是否打成执行 jar 包配置为参数项,默认为 false (即插件默认的打可执行 jar),外部执行 mvn package传入该参数值。如下示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 <project > <properties > <provider.package > false</provider.package > </properties > ... <build > <plugins > <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <configuration > <skip > ${provider.package}</skip > </configuration > </plugin > </plugins > </build > </project >
执行 mvn 命令,并传入 provider.package 参数
1 mvn clean package file-server -Dprovider.package=true
上面配置等同于:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 <project > <properties > <provider.package > false</provider.package > </properties > <build > <plugins > <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <executions > <execution > <goals > <goal > repackage</goal > </goals > <configuration > <skip > ${provider.package}</skip > </configuration > </execution > </executions > </plugin > </plugins > </build > </project >
或替换打包插件为 maven-jar-plugin,只打普通 jar包,但不推荐此方式,太死了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <build > <plugins > <plugin > <groupId > org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId > <artifactId > maven-jar-plugin</artifactId > </plugin > </plugins > </build >
配置示例 重新打包分类 默认情况下,repackage目标将用重新打包 的包替换原始原包 。 对于代表应用程序的模块来说,这是理智的行为,但是如果您的模块用作另一个模块的依赖项,则需要为重新包装的模块提供分类器。
这样做的原因是应用程序类打包在BOOT-INF/classes中,因此从属模块无法加载 repackaged 的 jar 的类。 如果需要保留原始包 ,并有可执行 jar 包,请按如下所示配置插件。
下示例配置会在 target 目录中创建 2 个 jar 文件,一个是原始 jar ,另一个是后缀带 exec 表示为可执行的 jar 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 <project > ... <build > ... <plugins > ... <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <version > 2.2.7.RELEASE</version > <executions > <execution > <id > repackage</id > <goals > <goal > repackage</goal > </goals > <configuration > <classifier > exec</classifier > </configuration > </execution > </executions > ... </plugin > ... </plugins > ... </build > ... </project >
如果使用的是spring-boot-starter-parent,则repackage目标将在 ID 为 repackage 的执行中自动执行。 在该设置中,只需指定配置,如下示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 <project > ... <build > ... <plugins > ... <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <executions > <execution > <id > repackage</id > <configuration > <classifier > exec</classifier > </configuration > </execution > </executions > ... </plugin > ... </plugins > ... </build > ... </project >
重新打包命名 如果需要重新打包的 jar 具有与项目的 artifactId 属性定义的本地名称不同的名称,只需使用标准 finalName,如下例所示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 <project > ... <build > <finalName > my-app</finalName > <plugins > ... <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <version > 2.2.7.RELEASE</version > <executions > <execution > <id > repackage</id > <goals > <goal > repackage</goal > </goals > </execution > </executions > ... </plugin > ... </plugins > ... </build > ... </project >
使用原始包 默认情况下,repackage目标将基于原始打包文件再次打包为可执行的文件,然后替换原始打包。 如果只需要部署原始 jar ,但仍能使用常规文件名运行应用程序,请按如下方式配置插件:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 <project > ... <build > ... <plugins > ... <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <version > 2.2.7.RELEASE</version > <executions > <execution > <id > repackage</id > <goals > <goal > repackage</goal > </goals > <configuration > <attach > false</attach > </configuration > </execution > </executions > ... </plugin > ... </plugins > ... </build > ... </project >
该配置将生成两个工件:原始工件 和由重新打包目标产生的可执行计数器部分。 将只 安装/部署 原始工程。
资源文件打包配置 打包时使用 resources 的 exclude 排除指定的资源文件,使用 maven-resources-plugin 将配置文件输出到外部目录。
Spring Boot 服务部署,通常把配置文件放到与 jar 包同级的 config 目录。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 <build > <resources > <resource > <filtering > true</filtering > <directory > src/main/resources</directory > <excludes > <exclude > **/application*.properties</exclude > <exclude > **/application*.yml</exclude > </excludes > </resource > </resources > <plugins > <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > </plugin > <plugin > <artifactId > maven-resources-plugin</artifactId > <executions > <execution > <id > copy-resources</id > <phase > package</phase > <goals > <goal > copy-resources</goal > </goals > <configuration > <resources > <resource > <directory > src/main/resources</directory > <includes > <include > **/application*.properties</include > <include > **/application*.yml</include > </includes > </resource > </resources > <outputDirectory > ${project.build.directory}/config</outputDirectory > </configuration > </execution > </executions > </plugin > </plugins > </build >
排除依赖 默认情况下,repackage和 run目标会包含任何定义在项目中的 provided依赖。Spring Boot 项目会认为 provided依赖是运行应用的容器所需的依赖。
其中一些依赖项可能根本不需要,应该从可执行jar 中排除。为了保持一致性,它们在运行应用程序时也不应该出现。
有两种方式可以排除在运行时 打包/使用 依赖项:
通过 groupId和 artifactId 排除一个指定的依赖。
指的 groupId 的来排除依赖。
下面所示通过指定 groupId 和 artifactId 排除 com.foo:bar依赖:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 <project > ... <build > ... <plugins > ... <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <version > 2.2.7.RELEASE</version > <configuration > <excludes > <exclude > <groupId > com.foo</groupId > <artifactId > bar</artifactId > </exclude > </excludes > </configuration > ... </plugin > ... </plugins > ... </build > ... </project >
下面所示,通过指定所属的 group来排除依赖:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 <project > ... <build > ... <plugins > ... <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <version > 2.2.7.RELEASE</version > <configuration > <excludeGroupIds > com.foo</excludeGroupIds > </configuration > ... </plugin > ... </plugins > ... </build > ... </project >
调试应用 默认情况下,运行(run)目标在分支过程中运行应用程序。 如果需要调试,则应添加必要的JVM 参数以启用远程调试。 以下配置将挂起该过程,直到调试器在端口 5005 上加入为止:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 <project > ... <build > ... <plugins > ... <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <version > 2.2.7.RELEASE</version > <configuration > <jvmArguments > -Xdebug -Xrunjdwp:transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=y,address=5005 </jvmArguments > </configuration > ... </plugin > ... </plugins > ... </build > ... </project >
这些参数也可以在命令行中指定,请确保参烤包装的正确,即:
1 mvn spring-boot:run -Dspring-boot.run.jvmArguments="-Xdebug -Xrunjdwp:transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=y,address=5005"
忽略集成测试 skip 属性允许完全跳过 Spring Boot maven 插件的执行应用。 此示例说明如何跳过带有命令行属性的集成测试,并仍然确保重新打包目标运行:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 <project > <properties > <skip.it > false</skip.it > ... </properties > ... <build > ... <plugins > ... <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <version > 2.2.7.RELEASE</version > <executions > <execution > <id > pre-integration-test</id > <goals > <goal > start</goal > </goals > <configuration > <skip > ${skip.it}</skip > </configuration > </execution > <execution > <id > post-integration-test</id > <goals > <goal > stop</goal > </goals > <configuration > <skip > ${skip.it}</skip > </configuration > </execution > </executions > </plugin > <plugin > <groupId > org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId > <artifactId > maven-failsafe-plugin</artifactId > <configuration > <skip > ${skip.it}</skip > </configuration > </plugin > ... </plugins > ... </build > </project >
默认情况下,将运行集成测试,但是此设置使可以按如下所示在命令行上轻松禁用它们:
1 mvn verify -Dskip.it = true
使用系统属性 可以使用 systemPropertyVariables指定系统属性。下面示例设置 property1 为 test,设置 property2为 42。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 <project > ... <build > <properties > <my.value > 42</my.value > </properties > ... <plugins > ... <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <version > 2.2.7.RELEASE</version > <configuration > <systemPropertyVariables > <property1 > test</property1 > <property2 > ${my.value}</property2 > </systemPropertyVariables > </configuration > ... </plugin > ... </plugins > ... </build > ... </project >
如果该值为空或未定义(即<my-property/>),则将系统属性设置为空字符串作为值。 Maven 修剪 pom 中指定的值,因此无法通过这种机制指定需要以空格开头 或结尾 的 System 属性:考虑改用 jvmArguments 。
任何 String 类型的 Maven 变量都可以作为系统属性 传递。 任何尝试传递任何其他 Maven 变量类型(例如 List 或URL 变量)的尝试都将导致变量表达式按字面值传递(未评估)。
jvmArguments 参数优先于上述机制定义的系统属性。 在以下示例中,property1 的值被覆盖:
1 mvn spring-boot:run -Dspring-boot.run.jvmArguments="-Dproperty1=overridden"
使用环境变量 可以使用 environmentVariables属性指定环境变量。下面示例设置 ENV1,ENV2,ENV3,ENV4环境变量:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 <project > ... <build > ... <plugins > ... <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <version > 2.2.7.RELEASE</version > <configuration > <environmentVariables > <ENV1 > 5000</ENV1 > <ENV2 > Some Text</ENV2 > <ENV3 /> <ENV4 > </ENV4 > </environmentVariables > </configuration > ... </plugin > ... </plugins > ... </build > ... </project >
如果该值为空或未定义(即<my-property/>),则将系统属性设置为空字符串作为值。 Maven 修剪 pom 中指定的值,因此无法通过这种机制指定需要以**空格 **开头 或 结尾 的环境变量。
用这种方法定义的环境变量优先于现有值。
使用应用参数 应用参数可通过 arguments 参数指定。下面示例设置 property1 和 property2=42参数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 <project > ... <build > <properties > <my.value > 42</my.value > </properties > ... <plugins > ... <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <version > 2.2.7.RELEASE</version > <configuration > <arguments > <argument > property1</argument > <argument > property2=${my.value}</argument > </arguments > </configuration > ... </plugin > ... </plugins > ... </build > ... </project >
在命令行上,参数用空格分隔,与jvmArguments 相同。 如果参数包含空格,请确保将其引号。 在以下示例中,有两个参数可用:property1 和 property2 = Hello World:
1 mvn spring-boot:run -Dspring-boot.run.arguments="property1 'property2=Hello World'"
集成测试随机端口 Spring Boot 测试集成的一个不错的功能是它可以为 Web 应用程序分配一个空闲端口。 当使用插件的启动目标时,Spring Boot 应用程序将单独启动,因此很难将实际端口传递给集成测试本身。
下面的示例展示了如何使用 build-helper-plugin 实现相同的功能:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 <project > ... <build > ... <plugins > ... <plugin > <groupId > org.codehaus.mojo</groupId > <artifactId > build-helper-maven-plugin</artifactId > <executions > <execution > <id > reserve-tomcat-port</id > <goals > <goal > reserve-network-port</goal > </goals > <phase > process-resources</phase > <configuration > <portNames > <portName > tomcat.http.port</portName > </portNames > </configuration > </execution > </executions > </plugin > <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <version > 2.2.7.RELEASE</version > <executions > <execution > <id > pre-integration-test</id > <goals > <goal > start</goal > </goals > <configuration > <arguments > <argument > --server.port=${tomcat.http.port}</argument > </arguments > </configuration > </execution > <execution > <id > post-integration-test</id > <goals > <goal > stop</goal > </goals > </execution > </executions > </plugin > <plugin > <groupId > org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId > <artifactId > maven-failsafe-plugin</artifactId > <configuration > <systemPropertyVariables > <test.server.port > ${tomcat.http.port}</test.server.port > </systemPropertyVariables > </configuration > </plugin > ... </plugins > ... </build > </project >
现在,可以在任何集成测试中检索test.server.port系统属性,以创建指向服务器的正确 URL。
指定激活配置文件 可以使用 profiles 参数指定要用于特定应用程序的活动配置文件。以下配置启用foo和bar配置文件:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 <project > ... <build > ... <plugins > ... <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <version > 2.2.7.RELEASE</version > <configuration > <profiles > <profile > foo</profile > <profile > bar</profile > </profiles > </configuration > ... </plugin > ... </plugins > ... </build > ... </project >
同样可以在命令行中指定 profiles,多个配置文件使用逗号(,)分隔:
1 mvn spring-boot:run -Dspring-boot.run.profiles=foo,bar
生成构建信息 如果存在META-INF / build-info.properties文件,Spring Boot Actuator 将显示与构建相关的信息。 build-info目标生成带有项目坐标和构建时间的文件。 它还允许您添加任意数量的其他属性:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 <project > ... <build > ... <plugins > ... <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <version > 2.2.7.RELEASE</version > <executions > <execution > <goals > <goal > build-info</goal > </goals > <configuration > <additionalProperties > <encoding.source > UTF-8</encoding.source > <encoding.reporting > UTF-8</encoding.reporting > <java.source > ${maven.compiler.source}</java.source > <java.target > ${maven.compiler.target}</java.target > </additionalProperties > </configuration > </execution > </executions > ... </plugin > ... </plugins > ... </build > ... </project >
此配置将在预期位置生成带有四个附加键的build-info.properties文件。 请注意,maven.compiler.source和maven.compiler.target应该是项目中可用的常规属性。 它们将按照期望进行插值。
相关参考
官方:Spring Boot 创建可执行 Jar Maven常用插件整理 Maven Surefire Plugin(JUnit篇) SpringBoot 打包的 jar 包与普通的 jar 包有什么区别 Spring Boot 打包,分离依赖jar,配置文件